Entropy(S) is the amount of disorder in a system. Solids tend to have low entropy, liquids higher entropy and gases the highest entropy. Single elements generally have lower entropy than compounds. Since entropy values are needed in determining whether or not a reaction is spontaneous, actual calculations need to be made.
To calculate the change in entropy (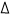 S)
for a reaction you must find the difference between the entropy
of the reactants and the entropy of the products. S)
for a reaction you must find the difference between the entropy
of the reactants and the entropy of the products.
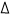 S
= S°(products) – S°(reactants) S
= S°(products) – S°(reactants)
|
For example:
Calculate the
change in entropy for the following reaction:
Ca + H2O  Ca(OH)2
+ H2 Ca(OH)2
+ H2
First balance the equation:
Ca + 2 H2O  Ca(OH)2
+ H2 Ca(OH)2
+ H2
Determine the entropy for the products and the reactants:
Ca + 2 H2O  Ca(OH)2
+ H2 Ca(OH)2
+ H2
41.4 + 2 (69.9)  75.9
+ 130.5 75.9
+ 130.5
181.2
 206.4 206.4
|
Substance |
S°
(J/mol K) |
Ca (s) |
41.4 |
H2O (l) |
69.9 |
Ca(OH)2 (s) |
75.9 |
H2 (g) |
130.5 |
|
| |
Calculate the 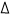 S for the reaction using the formula from above: S for the reaction using the formula from above:
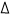 S = S°(products) – S°(reactants) S = S°(products) – S°(reactants)
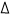 S = 206.4 – 181.2 S = 206.4 – 181.2
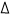 S = 25.2 J/K; entropy increases S = 25.2 J/K; entropy increases |